Global HTML Attributes: Essential Information for Web Developers
Master the Fundamentals of Adding Extra Information to HTML Elements
What is HTML?
HTML is an acronym for Hypertext Markup Language. It is a standard markup language that is used for creating web pages.
It is the code that is used to structure a web page and its content. This content can be structured within a paragraph, links, etc. using elements, links, tags, and attributes.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is responsible for maintaining and developing HTML specifications and providing regular updates.
NB: HTML is not a programming language
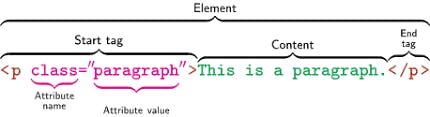
Parts that make up an HTML element
HTML elements are what make up the HTML document in general. The HTML element is a piece of markup language that is used to write HTML content.
Here is a link to all the HTML tags (W3Schools)
Contents in an HTML is wrapped within a tag.
<tagname attributes="">Place your content here...</tagname>
An HTML document is made up of a tag, an attribute, and, the content which contains what is to be displayed.
Tag: This indicates the beginning and end of an HTML element in an HTML document.
Attributes: These are special words that are used inside the opening tag to control the behavior of the HTML elements. This serves as the property of the elements. There are numerous attributes to control the properties of the HTML element.
Here is a list of various HTML attributes
Here is an example of an HTML element
<h1 class="main-heading">This is a heading</h1>
Global Attributes
Global attributes are attributes that can be used in all HTML elements except empty tags (i.e tags that do not have closing tags). These attributes can be used in any tag regardless of what elements. These attributes control the general properties of a text or display such as language, style, direction, etc.
Class
The class attribute is used in pointing tags in a stylesheet or JavaScript. The class attribute is like a pointer which is used to reference the elements from other sources e.g. CSS, JavaScript etc. to effect changes.
NB: Multiple class names can be used on one element. For example if, we want to use a class name to change the main-heading class to red and the text to green.
Id
The id is a unique identifier that is used to identify a single HTML element. The main difference between an id and a class is that an id can only target one element, but a class can target multiple classes.
We can also use the id to perform the same operation
Lang
This attribute specifies the language of the element's content. This is scarcely used in the body portion of the HTML layout, but it is commonly used in the meta tag. It is important for semantic meaning. I'll be discussing more of this in my upcoming article title "Aria Roles". For us to use this attribute, we include it in the opening tag of our element and specify the language we are using.
NB: Using this attribute does not automatically translate our content, as we need to write the language plainly and correctly.
Syntax
<tagname lang="language_code">Write your content here ........ </tagname>
The language code specfies what language we are using.
Here is a full list of the language(s) and their ISO codes
Here is a sample code
Style
The style attribute is an inline method of applying styles to our HTML contents. Although this method is scarcely used and highly discouraged while writing codes, it is still a valid way of styling our content.
Syntax
<tagname style="style_definitions">Write your content here...</tagname>
Our style definitions can be height, width, position, display, color, text-align etc. More of this will be discussed in our CSS articles.
Here is a code sample,
Dir
The dir attribute is used to set the base direction of a text for display. This attribute is very important for text that supports right-to-left scripts e.g. Arabic, Hebrew etc.
Syntax
<tagname dir="text-direction">Write your content here...</tagname>
The attribute's value (text-direction) can be of three values, viz
ltr - left-to-right. This reads our text from right to left
rtl- right-to-left. This reads our text from left to write
auto - lets the browser figure out the text-direction, based on the content
Here is an example code
Data-*
This is the last but not the least attribute and this attribute helps us to embed a custom data attributes on an HTML elements.
Syntax
<tagname data-{attribute}="value">Write your content here...</tagname>
NB: Anything can be used in the curly braces to pass the required data.
This data can be used for a wide range of functions in both CSS and JavaScript.
Here is an example,
Conclusion
In conclusion, global HTML attributes provide a quick and easy way to add extra information to HTML elements. They can be used to define the language of the document, set the styles for all elements, provide information about accessibility, and much more. Understanding and utilizing these attributes can greatly enhance the functionality and accessibility of a website. As web development continues to evolve, it's important to stay informed on the latest techniques and tools available, and global HTML attributes are certainly worth adding to your toolkit.
Thank you for reading 🙏🙏.
You can follow me on the following platforms:
Twitter 🐦: @nwokporo_ebuka
LinkedIn ⚡: @chukwuebuka_nwokporo
GitHub 🚀: @ebukvick
Hashnode 📗: Nwokporo Chukwuebuka